File:Microquasar GRO J1655-40.tif

Original file (3,000 × 2,400 pixels, file size: 1.8 MB, MIME type: image/tiff)
Captions
Captions
Summary[edit]
| DescriptionMicroquasar GRO J1655-40.tif |
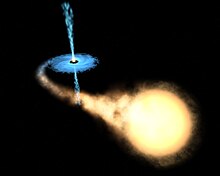
GRO J1655-40 (in blue) is the second so-called 'microquasar' discovered in our Galaxy. Microquasars are black holes of about the same mass as a star. They behave as scaled-down versions of much more massive black holes that are at the cores of extremely active galaxies, called quasar. Their masses can range from 3.5 to approximately 15 times the mass of our Sun. GRO J1655-40 is the second so-called 'microquasar' discovered in our Galaxy. Microquasars are black holes of about the same mass as a star. They behave as scaled-down versions of much more massive black holes that are at the cores of extremely active galaxies, called quasars. Astronomers have known about the existence of stellar-mass black holes since the early 1970s. Their masses can range from 3.5 to approximately 15 times the mass of our Sun. Using Hubble data, astronomers were able to describe the black-hole system. The companion star had apparently survived the original supernova explosion that created the black hole. It is an ageing star that completes an orbit around the black hole every 2.6 days. It is being slowly devoured by the black hole. Blowtorch-like jets (shown in blue) are streaming away from the black-hole system at 90% of the speed of light. |
|||
| Date | 18 November 2002, 15:00 | |||
| Source | https://esahubble.org/images/heic0211i/ | |||
| Author | ESA, NASA and Felix Mirabel (the French Atomic Energy Commission & the Institute for Astronomy and Space Physics/Conicet of Argentina) | |||
| Permission (Reusing this file) |
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International license. Attribution: ESA/Hubble
|
|||
| Other versions |
 |
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 21:49, 23 May 2023 |  | 3,000 × 2,400 (1.8 MB) | Юрий Д.К. (talk | contribs) | {{Information |Description=GRO J1655-40 (in blue) is the second so-called 'microquasar' discovered in our Galaxy. Microquasars are black holes of about the same mass as a star. They behave as scaled-down versions of much more massive black holes that are at the cores of extremely active galaxies, called quasar. Their masses can range from 3.5 to approximately 15 times the mass of our Sun. GRO J1655-40 is the second so-called 'microquasar' discovered in our Galaxy. Microquasars are black hole... |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage on Commons
There are no pages that use this file.
Metadata
This file contains additional information such as Exif metadata which may have been added by the digital camera, scanner, or software program used to create or digitize it. If the file has been modified from its original state, some details such as the timestamp may not fully reflect those of the original file. The timestamp is only as accurate as the clock in the camera, and it may be completely wrong.
| Width | 3,000 px |
|---|---|
| Height | 2,400 px |
| Bits per component |
|
| Compression scheme | LZW |
| Pixel composition | RGB |
| Number of components | 3 |
| Number of rows per strip | 1 |
| Horizontal resolution | 300 dpi |
| Vertical resolution | 300 dpi |
| Data arrangement | chunky format |
| Software used | Adobe Photoshop 7.0 |
| File change date and time | 09:55, 13 November 2002 |
| Color space | Uncalibrated |

