File:Saturn's A Ring From the Inside Out.jpg
Saturn's_A_Ring_From_the_Inside_Out.jpg (691 × 482 pixels, file size: 41 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
Captions
Captions
Summary[edit]
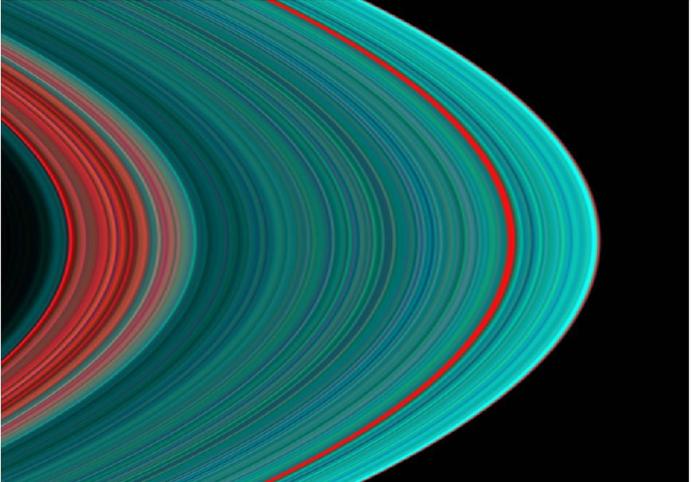
| DescriptionSaturn's A Ring From the Inside Out.jpg | An image of Saturn's A Ring, taken by the Cassini Orbiter using an Ultraviolet Imaging Spectrograph. |
| Date |
Unknown date Unknown date |
| Source | http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05075 |
| Author | NASA/JPL/University of Colorado |
This image or video was catalogued by Jet Propulsion Laboratory of the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) under Photo ID: PIA05075. This tag does not indicate the copyright status of the attached work. A normal copyright tag is still required. See Commons:Licensing. Other languages:
العربية ∙ беларуская (тарашкевіца) ∙ български ∙ català ∙ čeština ∙ dansk ∙ Deutsch ∙ English ∙ español ∙ فارسی ∙ français ∙ galego ∙ magyar ∙ հայերեն ∙ Bahasa Indonesia ∙ italiano ∙ 日本語 ∙ македонски ∙ മലയാളം ∙ Nederlands ∙ polski ∙ português ∙ русский ∙ sicilianu ∙ slovenščina ∙ Türkçe ∙ українська ∙ 简体中文 ∙ 繁體中文 ∙ +/− |
Original Caption Released with Image[edit]
The best view of Saturn's rings in the ultraviolet indicates there is more ice toward the outer part of the rings, than in the inner part, hinting at the origins of the rings and their evolution.
Images taken during the Cassini spacecraft's orbital insertion on June 30 show compositional variation in the A, B and C rings. From the inside out, the "Cassini Division" in faint red at left is followed by the A ring in its entirety. The Cassini Division at left contains thinner, dirtier rings than the turquoise A ring, indicating a more icy composition. The red band roughly three-fourths of the way outward in the A ring is known as the Encke gap.
The ring system begins from the inside out with the D, C, B and A rings followed by the F, G and E rings. The red in the image indicates sparser ringlets likely made of "dirty," and possibly smaller, particles than in the icier turquoise ringlets.
This image was taken with the Ultraviolet Imaging Spectrograph instrument, which is capable of resolving the rings to show features up to 97 kilometers (60 miles) across, roughly 100 times the resolution of ultraviolet data obtained by the Voyager 2 spacecraft.
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Cassini-Huygens mission for NASA's Office of Space Science, Washington, D.C. The Cassini orbiter was designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The Ultraviolet Imaging Spectrograph was built at, and the team is based at the University of Colorado, Boulder, Colo.
For more information, about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit, http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov and the Ultraviolet Imaging Spectrograph team home page, http://lasp.colorado.edu/cassini/.
Licensing[edit]
| Public domainPublic domainfalsefalse |
| This file is in the public domain in the United States because it was solely created by NASA. NASA copyright policy states that "NASA material is not protected by copyright unless noted". (See Template:PD-USGov, NASA copyright policy page or JPL Image Use Policy.) |  | |
 |
Warnings:
|
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 21:06, 13 December 2007 |  | 691 × 482 (41 KB) | Boricuaeddie (talk | contribs) | {{Information |Description=An image of Saturn's A Ring, taken by the Cassini Orbiter using an Ultraviolet Imaging Spectrograph. |Source=http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05075 |Date=Unknown |Author=NASA/JPL/University of Colorado |Permission= |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage on Commons
The following page uses this file:
File usage on other wikis
The following other wikis use this file:
- Usage on az.wikipedia.org
- Usage on cs.wikipedia.org
- Usage on en.wikipedia.org
- Usage on en.wikiversity.org
- Usage on es.wikipedia.org
- Usage on es.wikinews.org
- Usage on eu.wikipedia.org
- Usage on fa.wikipedia.org
- Usage on fr.wikipedia.org
- Usage on glk.wikipedia.org
- Usage on hi.wikipedia.org
- Usage on hy.wikipedia.org
- Usage on id.wikipedia.org
- Usage on it.wikipedia.org
- Usage on ja.wikipedia.org
- Usage on mk.wikipedia.org
- Usage on no.wikipedia.org
- Usage on pt.wikibooks.org
- Usage on rm.wikipedia.org
- Usage on stq.wikipedia.org
- Usage on vi.wikipedia.org
Metadata
This file contains additional information such as Exif metadata which may have been added by the digital camera, scanner, or software program used to create or digitize it. If the file has been modified from its original state, some details such as the timestamp may not fully reflect those of the original file. The timestamp is only as accurate as the clock in the camera, and it may be completely wrong.
| _error | 0 |
|---|