File:BlackHoleMovementsmoother.gif

Original file (800 × 800 pixels, file size: 6.7 MB, MIME type: image/gif, looped, 94 frames, 3.8 s)
Captions
Captions
Summary[edit]
| DescriptionBlackHoleMovementsmoother.gif |
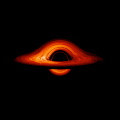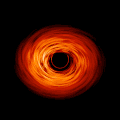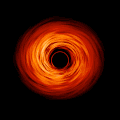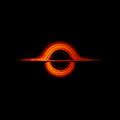
English: This movie shows a complete revolution around a simulated black hole and its accretion disk following a path that is perpendicular to the disk. The black hole’s extreme gravitational field redirects and distorts light coming from different parts of the disk, but exactly what we see depends on our viewing angle. The greatest distortion occurs when viewing the system nearly edgewise.
This new visualization of a black hole illustrates how its gravity distorts our view, warping its surroundings as if seen in a carnival mirror. The visualization simulates the appearance of a black hole where infalling matter has collected into a thin, hot structure called an accretion disk. The black hole’s extreme gravity skews light emitted by different regions of the disk, producing the misshapen appearance. Bright knots constantly form and dissipate in the disk as magnetic fields wind and twist through the churning gas. Nearest the black hole, the gas orbits at close to the speed of light, while the outer portions spin a bit more slowly. This difference stretches and shears the bright knots, producing light and dark lanes in the disk. Viewed from the side, the disk looks brighter on the left than it does on the right. Glowing gas on the left side of the disk moves toward us so fast that the effects of Einstein’s relativity give it a boost in brightness; the opposite happens on the right side, where gas moving away us becomes slightly dimmer. This asymmetry disappears when we see the disk exactly face on because, from that perspective, none of the material is moving along our line of sight. Closest to the black hole, the gravitational light-bending becomes so excessive that we can see the underside of the disk as a bright ring of light seemingly outlining the black hole. This so-called “photon ring” is composed of multiple rings, which grow progressively fainter and thinner, from light that has circled the black hole two, three, or even more times before escaping to reach our eyes. Because the black hole modeled in this visualization is spherical, the photon ring looks nearly circular and identical from any viewing angle. Inside the photon ring is the black hole’s shadow, an area roughly twice the size of the event horizon — its point of no return. Simulations and movies like these really help us visualize what Einstein meant when he said that gravity warps the fabric of space and time. |
| Date | |
| Source | https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/13326 |
| Author | NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center/Jeremy Schnittman |
| Other versions |
|
Licensing[edit]
| Public domainPublic domainfalsefalse |
| This file is in the public domain in the United States because it was solely created by NASA. NASA copyright policy states that "NASA material is not protected by copyright unless noted". (See Template:PD-USGov, NASA copyright policy page or JPL Image Use Policy.) |  | |
 |
Warnings:
|
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 13:48, 7 July 2023 | 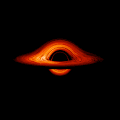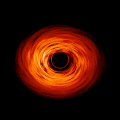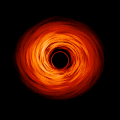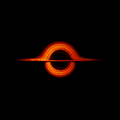 | 800 × 800 (6.7 MB) | ILVSM (talk | contribs) | Uploaded while editing "Чёрная дыра" on ru.wikipedia.org |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage on Commons
There are no pages that use this file.
File usage on other wikis
The following other wikis use this file:
- Usage on ru.wikipedia.org